Curious about what sulfur does for plants? Well, look no further! Sulfur plays a vital role in the growth and development of plants, and its benefits are truly remarkable. From aiding in the formation of essential plant proteins to enhancing nutrient uptake, sulfur is an essential nutrient that plants simply cannot thrive without.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of sulfur and explore its impact on plant health. So, get ready to uncover the many wonders of what sulfur does for plants!
What Does Sulfur Do for Plants?
Plants are remarkable organisms that rely on various nutrients to grow and thrive. While we often associate macronutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium with plant health, sulfur is another essential element that plays a crucial role in their development.
Sulfur is needed in smaller quantities compared to macronutrients, but its significance should not be overlooked. In this article, we will explore the incredible benefits of sulfur for plants and understand why it is a vital nutrient for their overall well-being.
The Importance of Sulfur in Plant Nutrition
Sulfur is one of the essential macronutrients required by plants. It is classified as a secondary macronutrient because plants need it in relatively lower amounts than nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
However, sulfur is no less important for healthy plant growth. It is involved in various physiological processes and serves as a building block for essential compounds that plants need to thrive.
Sulfur’s Role in Protein Formation
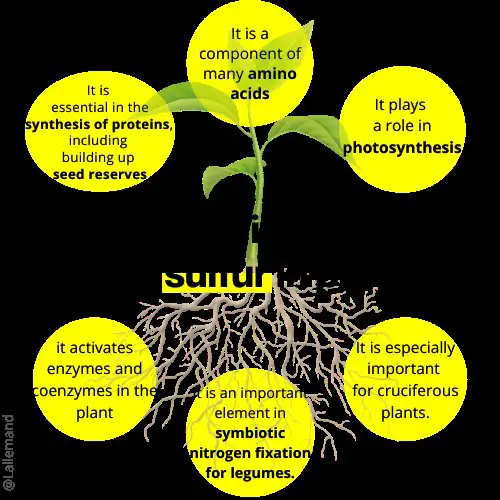
Proteins are the building blocks of life, and sulfur is a vital component in their formation. Sulfur-containing amino acids, such as cysteine and methionine, are crucial for the synthesis of proteins.
These proteins are responsible for various physiological functions, including enzyme activity, chlorophyll formation, and defense mechanisms against pests and diseases.
Without sufficient sulfur, plants would struggle to produce the necessary proteins for their growth and development.
Sulfur’s Role in Chlorophyll Synthesis
Chlorophyll is the green pigment responsible for capturing sunlight during photosynthesis. It allows plants to convert light energy into chemical energy, fueling their growth and providing essential oxygen for the environment. Sulfur is a critical element in the synthesis of chlorophyll molecules.
Without adequate sulfur, plants may suffer from chlorosis, a condition characterized by yellowing leaves due to reduced chlorophyll production. By ensuring sufficient sulfur availability, plants can maintain healthy chlorophyll levels and maximize their photosynthetic potential.
Sulfur’s Role in Nutrient Uptake and Efficiency
Sulfur plays a vital role in the overall nutrient uptake and efficiency of plants. It influences the permeability and selectivity of cell membranes, allowing nutrients to enter plant cells effectively.
Additionally, sulfur is involved in the synthesis of vitamins and enzymes that are necessary for nutrient metabolism. By optimizing nutrient uptake and utilization, sulfur enhances a plant’s ability to absorb and utilize other essential nutrients, promoting overall growth and development.
Read More: About Do Peace Lilies Have a Scent?
Sulfur’s Role in Stress Tolerance
Plants often face various environmental stresses, including drought, heat, and disease. Sulfur, with its diverse functions, also contributes to a plant’s ability to withstand these stresses.
It helps in the formation of stress-related compounds, such as phytoalexins and antioxidants, which protect plants against pathogens and oxidative damage.
Sulfur enhances a plant’s resilience, allowing it to withstand adverse conditions and maintain its vitality.
Signs of Sulfur Deficiency in Plants
Identifying sulfur deficiency in plants is crucial for timely intervention. Lack of sufficient sulfur can manifest in several ways, and recognizing these signs can help address the issue effectively.
Some common symptoms of sulfur deficiency include:
- Yellowing of younger leaves while the veins remain green
- Stunted growth and reduced plant vigor
- Premature leaf drop and poor fruit development
- Delayed flowering and limited seed production
- Increased susceptibility to pests and diseases
If you notice these symptoms in your plants, it is essential to consider sulfur supplementation to correct the deficiency and restore their health.
Sulfur Sources for Plants
To ensure sufficient sulfur supply for plants, it is important to understand the different sources available. Here are some common sulfur sources used in agriculture and gardening:
Organic Sources:
- Manure: Livestock manure, such as poultry manure or cow dung, contains sulfur and other essential nutrients. It can be applied as organic fertilizer to improve soil fertility and sulfur availability.
- Compost: Composting organic materials, such as kitchen scraps or yard waste, can provide plants with a slow-release source of sulfur. Adding compost to the soil enhances its overall nutrient content.
Inorganic Sources:
- Sulfate Fertilizers: Inorganic fertilizers like ammonium sulfate or potassium sulfate are common sources of sulfur. These fertilizers are water-soluble and allow for quick uptake by plants.
- Gypsum: Gypsum is a calcium sulfate compound that not only supplies sulfur but also improves soil structure and drainage.
Applying Sulfur for Plant Growth
When it comes to applying sulfur to plants, it is crucial to consider the specific requirements of different plant species and the existing soil conditions. Some general guidelines for sulfur application include:
Soil Testing:
- Before applying sulfur, conducting a soil test is recommended to determine the existing sulfur levels and pH of the soil. This will help in determining the appropriate amount of sulfur required and prevent over-application.
Timing and Method:
- Applying sulfur in a timely manner is crucial for optimal results. It is generally recommended to apply sulfur during the growing season or before planting to ensure its availability when plants need it the most.
- The method of sulfur application can vary depending on the specific requirements. It can be applied as a top dressing, incorporated into the soil during preparation, or dissolved in irrigation water for foliar application.
Rate of Application:
- The rate of sulfur application depends on various factors, including soil type, plant requirements, and existing sulfur levels. It is essential to follow recommended guidelines or consult with agricultural experts for precise dosage information.
Sulfur is a vital nutrient for plants, contributing to their overall growth and development. From protein synthesis to chlorophyll formation, sulfur plays a significant role in essential physiological processes. By ensuring sufficient sulfur availability, plants can improve their nutrient uptake, enhance stress tolerance, and maintain optimal health.
Understanding the signs of sulfur deficiency and using appropriate sulfur sources and application methods are essential for promoting healthy plant growth. With the knowledge gained from this article, you can now unleash the power of sulfur and maximize the potential of your plants.
Read More: About How to Get Big Pothos Leaves
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Sulfur plays a crucial role in plant growth and development. It is an essential nutrient required for various metabolic processes. Here are some commonly asked questions about the role of sulfur in plants:
Sulfur is involved in the production of chlorophyll, which is essential for photosynthesis. It also plays a vital role in protein synthesis, enzyme activity, and the formation of plant structure.
Yes, sulfur deficiency can significantly impact plant growth. It can lead to yellowing of leaves, stunted growth, and reduced crop yields.
Sulfur helps in improving soil fertility by enhancing nutrient availability. It aids in the breakdown of organic matter and promotes the release of nutrients such as phosphorus and micronutrients.
Sulfur deficiency is often characterized by yellowing of leaves, especially in younger leaves. The symptoms may resemble nitrogen deficiency, but sulfur deficiency affects the overall plant growth differently.
Sulfur can be added to soil through the application of sulfur-containing fertilizers, such as elemental sulfur or sulfate-based fertilizers. These can be applied directly to the soil or incorporated into compost.
Yes, organic matter like compost, manure, and plant residues are natural sources of sulfur. When they decompose, they release sulfur into the soil, making it available to plants.
While sulfur is essential for plant growth, excessive amounts can be harmful. It can cause toxicity symptoms, such as leaf burn or necrosis. It is crucial to follow recommended application rates to avoid sulfur toxicity.
Certain plants, including cruciferous vegetables like cabbage, broccoli, and cauliflower, have a higher sulfur requirement compared to others. Brassicas, onions, and garlic are examples of plants that benefit from adequate sulfur levels.
Remember to always consult local agricultural extension services or experts for specific recommendations based on your plant species and soil conditions.
Final Thoughts
Sulfur plays a crucial role in enhancing plant health and growth. Firstly, it is an essential component of amino acids, proteins, and enzymes, which are vital for plant development. Additionally, sulfur aids in chlorophyll production, promoting photosynthesis and ensuring efficient energy conversion. Sulfur also contributes to the formation of strong cell walls, improving plant structure and resistance to disease and pests.
Moreover, sulfur is involved in nutrient uptake, facilitating the absorption of other essential elements. In summary, sulfur is essential for various plant functions, making it a critical nutrient for overall plant health and productivity.
Auto Amazon Links: No products found.
Perfect Plants Christmas Tree Saver 8oz. | Easy Use Xmas Tree Preserver Food | Have Healthy Green Christmas Trees All Holiday Season
$16.99 (as of February 11, 2026 00:40 GMT +00:00 - More info- Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
VEVOR Tree Watering Bags Slow Release, 4 Pack 16 Gallons Tree Watering Ring, Reusable Refillable Tree Irrigation Ring Water Bags, Heavy Duty Watering System for Shrub Tree Root Drip Irrigation
$29.99 (as of February 11, 2026 00:40 GMT +00:00 - More info- Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
Wilt-Pruf® Christmas Tree/Cutting Preserver Spray |Preserves Christmas Trees, Wreaths, Garlands, Cuttings and Carved Pumpkins | Reduces Needle Drop | Keeps Cut Trees Fresh Longer | Natural (32 oz)
$21.99 (as of February 11, 2026 00:40 GMT +00:00 - More info- Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
Mini Decorative Metal Watering Can, Set of 6, Height 1.97 inch, Cute Metal Jug for Hand Crafts,Garden Theme Parties, Home and Refrigerator Decor
$8.99 (as of February 11, 2026 00:40 GMT +00:00 - More info- Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
Rocky Mountain Goods Christmas Tree Food - 8 oz Tree Preservative - Reduce Needle Drop - Greener Scent - Fir, Pine, Spruce Trees - Extend Tree Life
$9.95 (as of February 11, 2026 00:40 GMT +00:00 - More info- Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
TERRO Ant Killer Bait Stations T300B - Liquid Bait to Eliminate Ants - Bait System - 12 Count Stations for Effective Indoor Ant Control
$11.97 (as of February 10, 2026 22:06 GMT +00:00 - More info- Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
Wagner's 53002 Farmer's Delight Wild Bird Food with Cherry Flavor, 10-Pound Bag
$12.48 (as of February 10, 2026 22:06 GMT +00:00 - More info- Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
OLANLY Dog Door Mat for Muddy Paws 30x20, Absorbs Moisture and Dirt, Absorbent Non-Slip Washable Doormat, Quick Dry Chenille Mud Mat for Dogs, Entry Indoor Entryway Carpet for Inside Floor, Grey
$9.49 (as of February 10, 2026 22:06 GMT +00:00 - More info- Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
Zevo Flying Insect Trap Official Refill Cartridges - Fits Both Zevo Trap & MAX Indoor Fly Trap - Authentic Trap+Lock Technology to Catch Gnats, House & Fruit Flies (4 Official Refill Cartridges)
$14.97 (as of February 10, 2026 22:06 GMT +00:00 - More info- Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.
Advion Cockroach Gel Bait, 4 Tubes x 30-Grams, 1 Plunger and 2 Tips, German Roach Insect Pest Control, Indoor and Outdoor Use, Roach Killer Gel for American, German and Other Major Cockroach Species
$25.62 (as of February 10, 2026 22:06 GMT +00:00 - More info- Product prices and availability are accurate as of the date/time indicated and are subject to change. Any price and availability information displayed on [relevant Amazon Site(s), as applicable] at the time of purchase will apply to the purchase of this product.